Lock picking is an intriguing skill that has captured the imagination of many, from locksmiths and security professionals to hobbyists and enthusiasts. While it is essential to emphasise the ethical considerations surrounding lock picking, understanding the principles and techniques involved can provide valuable insights into the mechanics of locks and enhance your overall understanding of security. In this comprehensive blog post, we will embark on a journey into the world of lock picking, exploring the fundamental principles, necessary tools, and step-by-step techniques to help beginners develop the skills required to master this captivating art.
The Foundation: Understanding Locks and Their Components
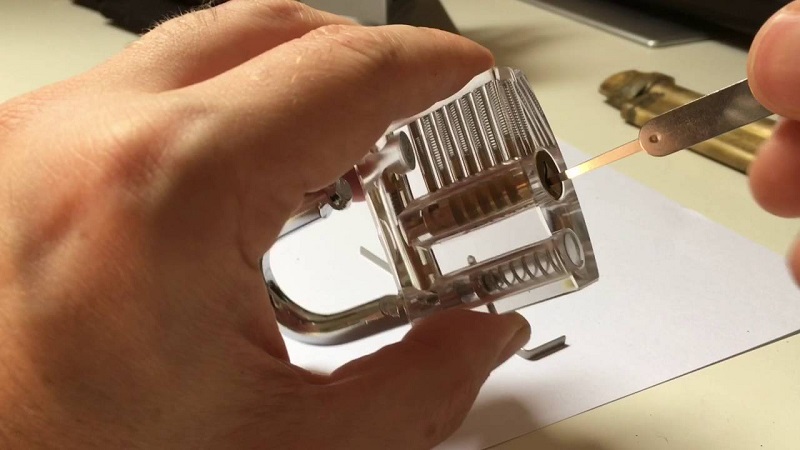
To effectively pick a lock, it is crucial to comprehend its inner workings. Most traditional locks, such as pin tumbler locks, are comprised of several key components:
- Keyway: The opening through which the key is inserted.
- Plug: The rotating component that contains the keyway and is connected to the locking mechanism.
- Pins: Thin metal cylinders that are divided into driver pins and key pins. The driver pins rest between the plug and the outer housing, while the key pins align with the cuts of the inserted key.
- Shear Line: The separation point between the plug and the outer housing, where the pins rest when the correct key is inserted.
By understanding these basic components, you can begin to visualise how the manipulation of pins within the lock allows for successful lock picking.
Essential Tools of the Trade
Before diving into the techniques, it’s important to gather the necessary tools for lock picking. While a professional lock picking set may contain numerous specialised tools, beginners can start with a simplified selection:
- Tension Wrench: This tool applies slight rotational pressure to the plug, simulating the action of a key turning.
- Pick: There are various types of picks, including the hook, rake, and diamond. These picks are used to manipulate the pins inside the lock.
- Torsion Wrench: Similar to a tension wrench, the torsion wrench is inserted into the plug and provides rotational force. It can be useful in certain situations where a tension wrench may not fit.
With these fundamental tools, you are ready to begin practicing the art of lock picking.
Basic Techniques for Pin Tumbler Locks
Pin tumbler locks are one of the most common types of locks, making them an ideal starting point for beginners. The following techniques will guide you through the process of picking pin tumbler locks:
- Applying Tension: Insert the tension wrench into the bottom of the keyway, applying slight rotational pressure in the direction that the key would turn.
- Locating Binding Pins: Gently insert the pick into the keyway and systematically test each pin by lifting it upward. Pay attention to pins that exhibit resistance or create a “click” sound when lifted.
- Setting Pins: Apply upward pressure on the binding pins while slowly releasing tension on the wrench. As each pin reaches the correct position, it will set into place, creating a slight movement in the plug.
- Repeat and Progress: Continue this process, alternating between applying tension, locating binding pins, and setting pins. With practice, you will develop a sense of feedback and timing required to successfully pick a lock.
Advanced Techniques and Additional Tools
As your skills progress, you may encounter locks that require more advanced techniques and additional tools. Some of these techniques include:
- Raking: Raking involves quickly and repeatedly manipulating the pins using a rake pick. This technique is often used for quick entry in non-pick-resistant locks or to set multiple pins simultaneously.
- Single Pin Picking: Single pin picking involves individually manipulating each pin to set it into place. This technique requires precision and finesse but offers greater control over the picking process.
- Specialised Picks: As you become more proficient, you may explore specialised picks such as dimple picks or wafer picks, designed for specific lock types.
Ethics and Legal Considerations
It is crucial to approach lock picking with a strong ethical framework and respect for the law. Lock picking should only be practiced on locks that you own or have explicit permission to pick. Engaging in unauthorised lock picking or using these skills for illegal purposes is strictly prohibited and can result in severe legal consequences.
Lock picking should be seen as a means of education, improving security awareness, and enhancing personal skill rather than as a tool for unlawful activities.
Mastering the art of lock picking is a journey that requires patience, practice, and a dedication to ethical principles. By understanding the fundamental principles of locks, acquiring the necessary tools, and practicing various techniques, beginners can develop the skills to manipulate pin tumbler locks effectively. However, it is important to remember the ethical and legal responsibilities associated with lock picking and to use this knowledge responsibly and lawfully.
As you embark on this fascinating journey, keep in mind that lock picking is an ongoing learning process. With dedication and persistence, you can unlock the secrets of locks, gaining a deeper understanding of security mechanisms and enhancing your overall knowledge in the field.